First step toward circular energy
Overview
Biomass is the general term for plant- and animal-derived bioresources. In bioenergy applications, these resources are burned or gasified directly.
Technological advances have enabled the efficient use of various bioresources.
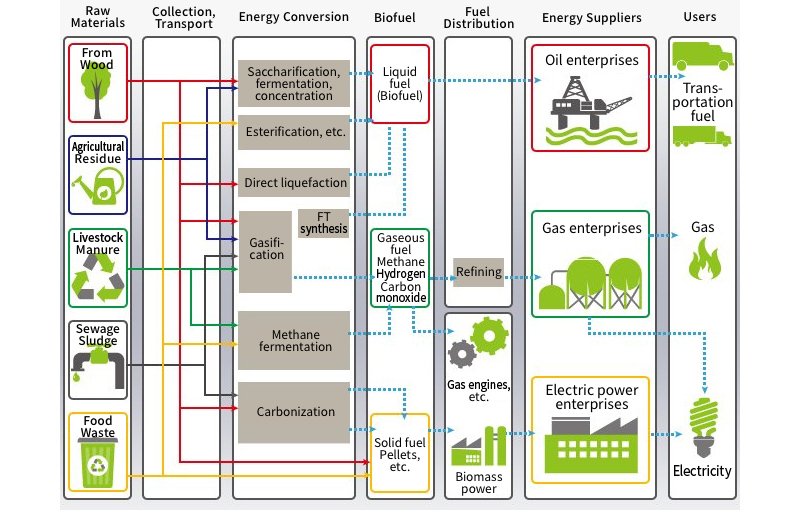
Approaches to bioenergy can be broadly classified as follows. One method involves anaerobic fermentation of substances such as sewage sludge or food, livestock, or agricultural waste to create methane gas that is used in gas engines or fuel cells to supply heat or electricity. Another involves burning solid materials such as wood waste, similar waste materials, or forest residue in boilers to produce steam for steam turbines that generate electricity. Additionally, liquid biofuels are used in diesel cogeneration.
Highlights
Addressing Climate Change
Power generation fueled by biomass resources—which absorb carbon dioxide through photosynthesis as they grow—is considered to be free of CO2 emissions under the Kyoto Protocol.
Building Circular Economies
Biomass power generation with waste as fuel both reduces waste and puts it to good use, contributing significantly to a circular economy.
From Collection of Biomass Feedstock to Supplying the Power Generated
For product inquiries, please submit the contact form.